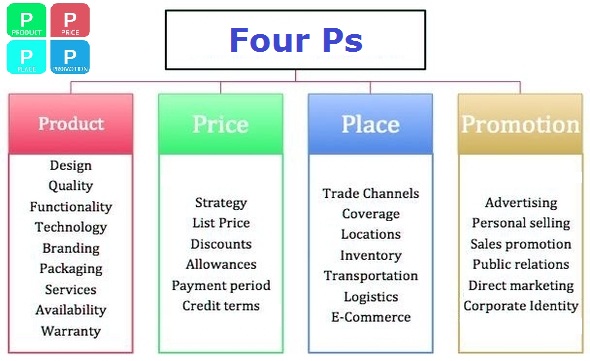
Marketing mix is a fundamental business tool that outlines the four key components of any product or service: product, price, promotion and place. Acting as a short-cut, the marketing mix allows marketers to easier envision an optimal brand’s offering. The framework was originally coined in the 1960’s by a marketer by the name of E. Jerome McCarthy and since then became popular and has been used throughout the world.
Product/Service
This category includes a wide range of offerings. In fact, a product or a service can be anything that satisfies a customer demand, whether tangible or intangible. For example, a car, a disposable razor or a software program – all fall under the tangible category. In order to create value for customers and the firm, marketers need to make decisions about the product, such as: brand, size, quality, features, packaging, warranty, etc. Once these key product characteristics have been identified, the marketing team can then move on to determining the price of the offering.A service, on the other hand, usually falls under an intangible category, such as a technical support experience, a haircut or a plane flight.
Price
Price is a crucial component of the marketing mix for two reasons. First, it is a major determinant of the company’s profit and therefore company’s success on the market. Secondly, it affects how valuable the customer finds the product or service. On the one hand, the less the customer has to give up in order to receive something, the more valuable he or she will perceive it to be. On the other hand, certain luxury goods and services (e.g. a high-end car, a business class flight, a designer dress, etc.) are sometimes perceived as more valuable as a result of their higher price.Aside from money, price also includes other things a customer is willing to give up in return for the product or services, such as time and effort.
From the marketer’s perspective, determining the price could also involve determining the following: discounts, allowances, costs, payment periods and credit terms.
Promotion
Promotion includes providing information and communicating value to potential customers. Such communication can be used to persuade and remind potential customers, influence and enhance their opinion of product or service, as well as elicit a response. The multiple methods of promotion include: advertising, public relations, sales promotion, celebrity endorsements, product placement and word-of-mouth. Marketers task is to determine which method(s) better suits the target audience.
Place
Of the 4P’s of the Marketing Mix, place is an often undervalued component. However, place refers to the distribution of goods or services from the manufacturer/provider to the consumer. This process includes multiple stakeholders and therefore involves higher risk. A few examples of such intermediate agencies are: marketing channels, retailer locations, supply chain, etc. Therefore, it is crucial to create a well-functioning logistics, so that the product or service is delivered on time and conveniently for the customer. To do that a mix of strategies like intensive distribution, selective distribution, exclusive distribution and franchising can be used.