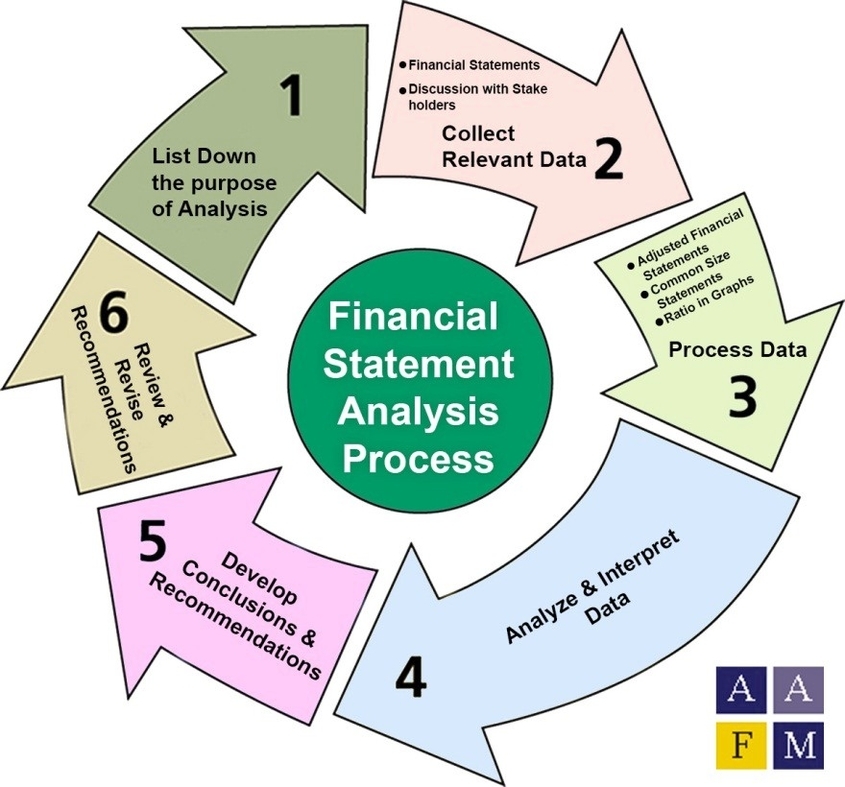
Financial statement analysis is the process of analyzing a company’s financial statements for decision-making purposes. It is used by internal and external stakeholders to evaluate business performance and value. Financial accounting calls for all companies to create a balance sheet, income statement, and cash flow statement, which form the basis for financial statement analysis.
There are three techniques that analysts use when analyzing financial statements: horizontal, vertical, and ratio analysis. Horizontal analysis compares data horizontally, by analyzing values of line items across two or more years. Vertical analysis looks at the vertical effects that line items have on other parts of the business and the businesss proportions. Ratio analysis uses important ratio metrics to calculate statistical relationships.
The balance sheet, income statement, and cash flow statement are the three main financial statements that companies create and maintain. They are interconnected and create different views of a companys activities and performance. The balance sheet is a report of a companys financial worth in terms of book value. It is broken into three parts to include a companys assets, liabilities, and shareholder equity. Short-term assets such as cash and accounts receivable can tell a lot about a companys operational efficiency; liabilities include the companys expense arrangements and the debt capital it is paying off; and shareholder equity includes details on equity capital investments and retained earnings from periodic net income.
The income statement is a report of a companys financial performance over a specific period of time. It is broken into two parts: revenue and expenses. Revenue is the money that a company earns from its operations, while expenses are the costs that a company incurs to generate revenue.
The cash flow statement is a report of a companys cash inflows and outflows over a specific period of time. It is broken into three parts: operating activities, investing activities, and financing activities. Operating activities include cash inflows and outflows from the companys primary operations. Investing activities include cash inflows and outflows from the companys investments. Financing activities include cash inflows and outflows from the companys financing activities.
