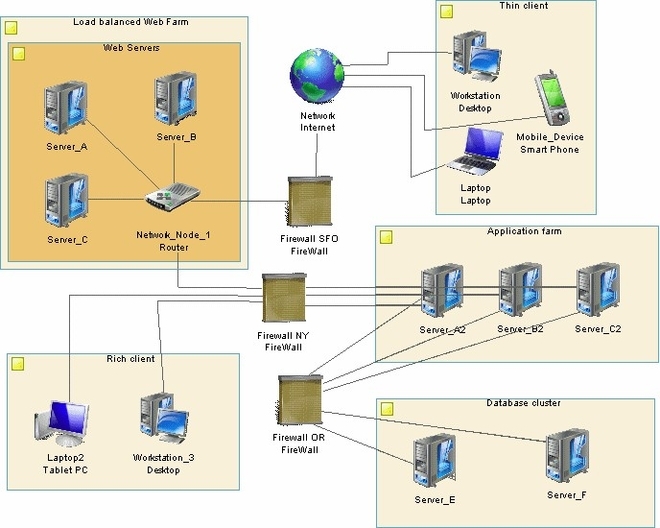
Infrastructure Architecture is a term used to describe the overall design of an organization’s information technology (IT) systems and infrastructure. It concerns the physical and logical components of an organization’s IT systems, including hardware, software, networks, and data storage. The goal of infrastructure architecture is to ensure that all of these components are properly aligned and integrated to support the business goals and objectives of the organization.
According to the Open Group Architecture Framework (TOGAF), infrastructure architecture connotes the architecture of the low-level hardware, networks, and system software (sometimes called “middleware”) that supports the applications software and business systems of an enterprise . However, infrastructure has a wider connotation in TOGAF.
Infrastructure architecture is a structured approach to dealing with the new infrastructure landscape that has emerged due to the rise in Big Data, cloud computing, and the diversity of remote devices. Ever-expanding integration, security, and information management issues are the newest challenges modern organizations face. Successful Infrastructure Architecture clarifies what functionality is required, by whom, and at what level of quality. This analysis facilitates informed decision-making in designing, constructing, and running an organization’s infrastructure. It allows businesses to use the right models quickly, leading to superior results. Great Infrastructure Architecture ensures trust: in SLAs, OLAs, and in customers who rely on accurate delivery times, accurate and timely invoicing, and reliable service delivery. This is true no matter what sector you are in.
Infrastructure architecture involves creating a detailed blueprint outlining the design and layout of an organization’s IT systems. This blueprint serves as a guide for developing and implementing the infrastructure. It includes information about the hardware and software components that will be used and the network and data storage systems. The infrastructure architecture also specifies the roles and responsibilities of the various stakeholders involved in developing and implementing the infrastructure, including IT staff, business units, and vendors.
One of the main benefits of having a well-defined infrastructure architecture is that it helps to ensure that the organization’s IT systems are scalable, flexible, and able to support the organization’s business needs. A well-designed infrastructure architecture can also help to reduce costs by streamlining processes and eliminating redundant systems and components. Additionally, a well-defined infrastructure architecture can help improve the security and reliability of an organization’s IT systems by providing a clear and consistent framework for developing and implementing security controls and protocols.
In summary, Infrastructure Architecture is
