Agile’s focus on delivering small, incremental improvements allows for quicker wins and boosts team morale. #QuickWins #Agile
Author Archives: admin
Strategy Pyramid Template
The Strategy Pyramid is a framework that helps organizations align their actions with their overall vision and mission. It is a guide for strategic planning and decision-making. The pyramid starts with the vision and mission at the top, which provide a clear and overarching direction for the organization. The next level is values, the guiding principles that shape the organization’s culture and behavior. Goals come next: specific, measurable objectives the organization aims to achieve. Strategy is the plan of action that outlines how the organization will achieve its goals. Finally, the action plan is the specific tactics and actions the organization will take to implement the strategy .
If you are interested in using the Strategy Pyramid for your organization, you can download a free PowerPoint template from StrategyPunk . The template is fully editable and can be customized with the specific information relevant to your strategy. You can also check out SlideEgg’s Strategy Pyramid PowerPoint Template and Google Slides .

Project management is like a puzzle
Project management is like a puzzle, and planning is the process of fitting all the pieces together. Take your time and do it right. #Planning #ProjectManagement #Success
The lack of stability and consistency resulting from excessive organizational changes can make it difficult for employees to establish routines and work effectively #Changes
The lack of stability and consistency resulting from excessive organizational changes can make it difficult for employees to establish routines and work effectively #Changes
Businesses that prioritize client experience invest in building strong customer relationships, fostering trust and loyalty over time #ClientExperience
Businesses that prioritize client experience invest in building strong customer relationships, fostering trust and loyalty over time #ClientExperience
The lack of clarity and direction resulting from excessive organizational changes can create a sense of aimlessness and apathy among employees, impacting their motivation and productivity #Changes
The lack of clarity and direction resulting from excessive organizational changes can create a sense of aimlessness and apathy among employees, impacting their motivation and productivity #Changes
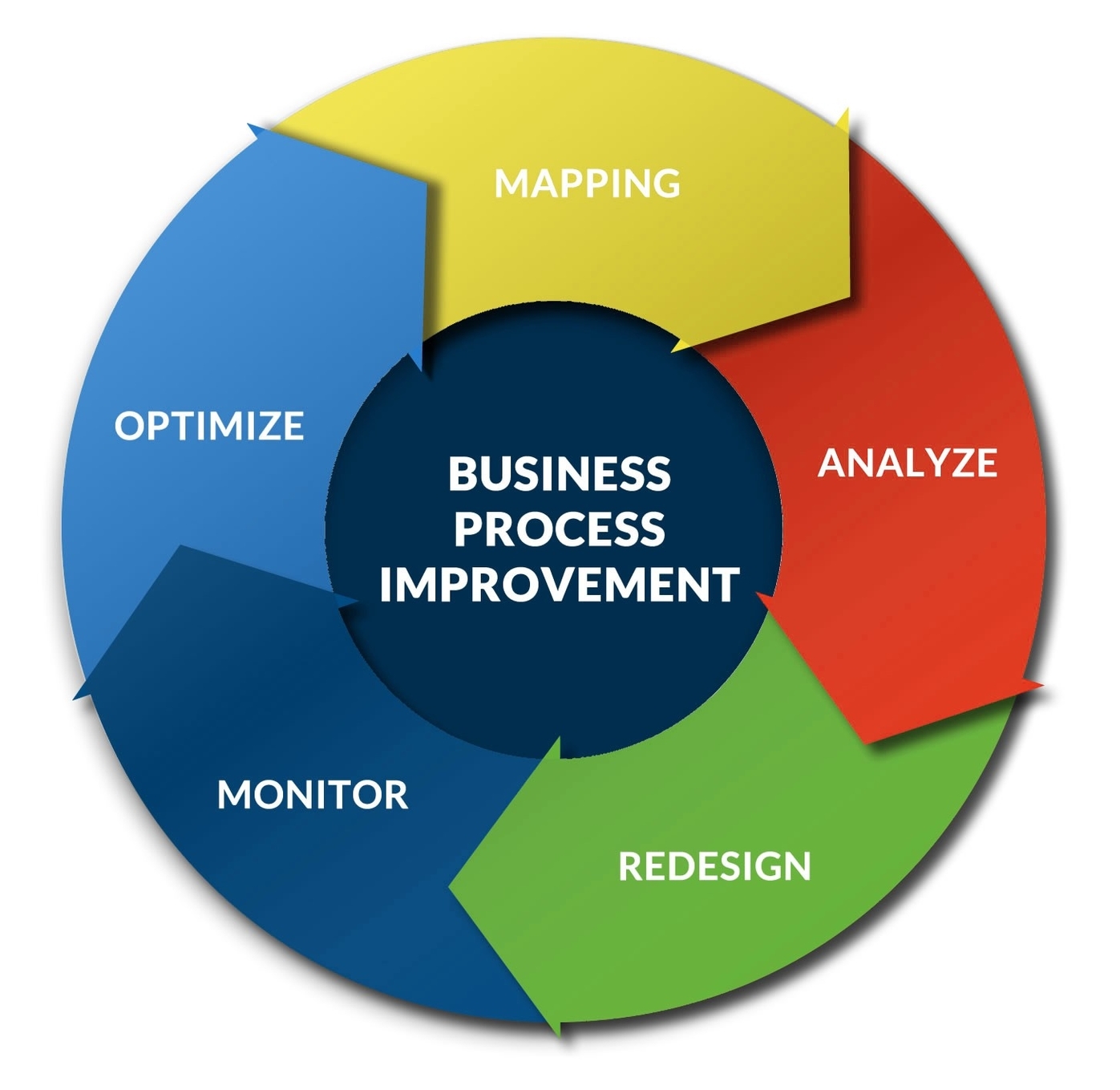
Business Process Improvement
Business Process Improvement (BPI) is a systematic approach of identifying, analyzing, and redesigning business processes to improve efficiency, effectiveness, and agility. It involves finding and solving problems in existing processes, such as inefficiencies, errors, waste, or delays. BPI can help businesses achieve various goals, such as reducing process time, improving output quality, cutting out waste, or increasing customer satisfaction.
There are different methodologies and steps for BPI, but the general idea is to map out the current processes, identify the areas that need improvement, implement changes, and measure the results. Some of the common BPI methodologies are Lean, Six Sigma, Kaizen, Business Process Reengineering, and Agile.
If you want to learn more about BPI, you can check out these resources:
– [What Is Process Improvement? Forbes Advisor](^1^)
– [A Guide to Business Process Improvement (With How-to Steps)](^3^)
– [Process Improvement | Definition, Fundamentals and Examples for 2024](^4^)
At the intersection of passion and profit lies the potential for impactful and sustainable businesses
At the intersection of passion and profit lies the potential for impactful and sustainable businesses. #ImpactfulBusinesses #Money
Waterfall’s linear approach can lead to ‘analysis paralysis,’ with teams spending too much time planning and not enough time doing
Waterfall’s linear approach can lead to ‘analysis paralysis,’ with teams spending too much time planning and not enough time doing. Agile values action over analysis. #ActionOverAnalysis #Agile
Scenario Planning Examples
Scenario planning is a strategic planning tool that helps decision-makers identify ranges of potential outcomes and impacts, evaluate responses, and manage for both positive and negative possibilities. It is a way to assert control over an uncertain world by identifying assumptions about the future and determining how your organization will respond. By visualizing potential risks and opportunities, businesses can become proactive versus simply reacting to events.
There are a number of templates and formalized frameworks for scenario planning, as we’ll discuss. For instance, NetSuite provides a comprehensive guide to scenario planning, including practical examples and steps to follow.
Operational scenario planning examples in a project-orientated business can include:
1. How a project will continue if key resources are unavailable.
2. What happens with resources and deadlines if new projects are added to the pipeline.
3. Courses of action if tasks take longer than planned.
4. Assessing the effect of work progressing at its current rate.
5. Asking what you might do if the cost of doing a task ends up being more than what you’d budgeted .
Another example of scenario planning is workforce planning. Workforce planning is the process of analyzing, forecasting, and planning workforce supply and demand. It involves identifying the skills and competencies required to meet business objectives, assessing the current workforce, and forecasting future workforce needs. Scenario planning can help organizations prepare for different scenarios that could impact their workforce, such as changes in the economy, new technologies, or shifts in the labor market. By developing plausible scenarios, organizations can identify potential workforce gaps and develop strategies to address them .
ales capacity planning is another example of scenario planning. Sales capacity planning is the process of determining the sales capacity required to meet business objectives. It involves analyzing historical sales data, forecasting future sales, and determining the resources required to achieve those sales. Scenario planning can help organizations prepare for different scenarios that could impact their sales capacity, such as changes in the economy, new competitors, or shifts in customer preferences. By developing plausible scenarios, organizations can identify potential sales gaps and develop strategies to address them .
trategic operational planning is yet another example of scenario planning. Strategic operational planning is the process of developing and implementing strategies to achieve business objectives. It involves analyzing the current state of the business, identifying opportunities for improvement, and developing strategies to achieve those improvements. Scenario planning can help organizations prepare for different scenarios that could impact their strategic operational planning, such as changes in the economy, new technologies, or shifts in customer preferences. By developing plausible scenarios, organizations can identify potential gaps in their strategic operational planning and develop strategies to address them .
In conclusion, scenario planning is a valuable tool for businesses to prepare for different scenarios that could impact their operations. By developing plausible scenarios, organizations can identify potential gaps and develop strategies to address them. There are a number of templates and formalized frameworks for scenario planning, and it’s important to choose a method that works for your team. Scenario planning is a way to assert control over an uncertain world by identifying assumptions about the future and determining how your organization will respond. By visualizing potential risks and opportunities, businesses can become proactive versus simply reacting to events .

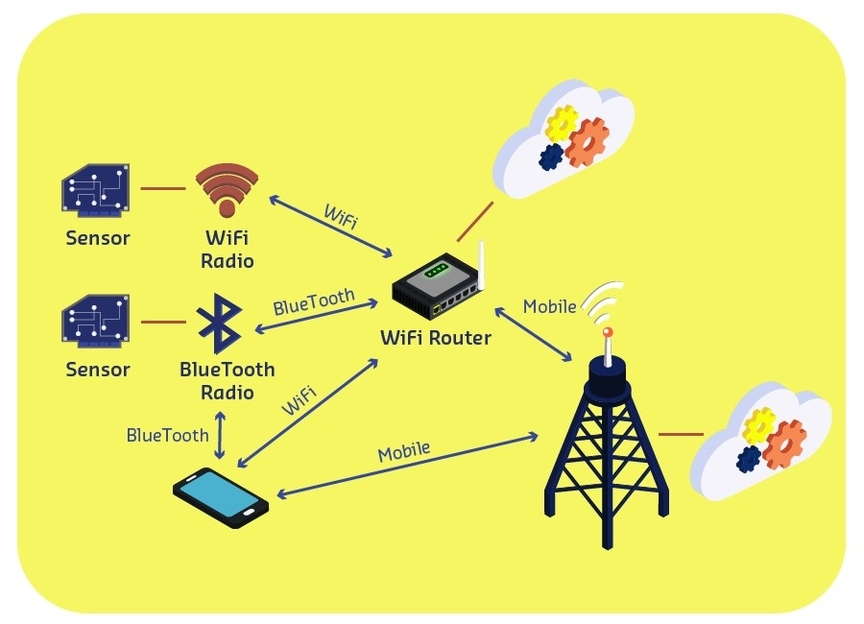
Wireless Technologies
Wireless technologies are methods of communication or data transmission that do not rely on wires or cables. They use electromagnetic waves, such as radio, infrared, or light, to send and receive information over the air. Wireless technologies have many applications and benefits, such as:
– They enable mobility and convenience for users, who can access wireless networks and devices from anywhere within the signal range.
– They reduce the cost and complexity of installation and maintenance, as they do not require physical infrastructure or wiring.
– They support a variety of devices and services, such as cellular phones, Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, GPS, satellite TV, and wireless chargers.
– They facilitate innovation and development of new technologies and solutions, such as 5G, IoT, and smart cities.
ome of the challenges and limitations of wireless technologies are:
– They are susceptible to interference, noise, and attenuation, which can degrade the quality and reliability of the signal.
– They have security and privacy risks, as wireless transmissions can be intercepted, eavesdropped, or hacked by unauthorized parties.
– They have regulatory and ethical issues, as wireless spectrum is a scarce and valuable resource that needs to be managed and allocated by the authorities.
– They have environmental and health impacts, as wireless devices and networks consume energy and emit radiation that may affect humans and other living organisms.
Wireless technologies are constantly evolving and improving, as new standards, protocols, and techniques are developed and implemented. Wireless technologies have transformed the way we communicate, work, learn, and entertain, and they will continue to shape the future of our society and economy.
This is a summary of wireless technologies in approximately 300
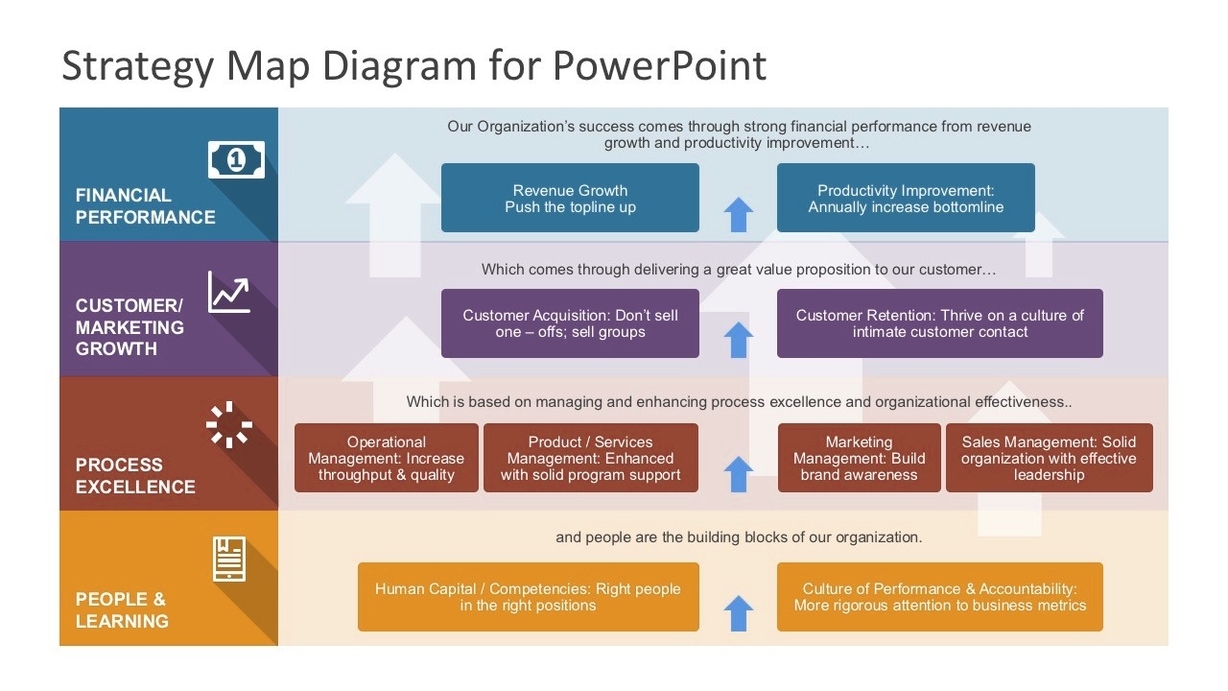
Strategy Map
A Strategy Map is a powerful strategic planning tool that helps organizations visualize their entire strategy on a single sheet of paper. It is a diagram that documents the strategic goals being pursued by an organization or management team . The technique of strategy mapping is designed to help a management team explore and discuss the strategy in more detail than they normally would. It helps develop highly effective strategies that can actually be implemented .
A strategy map is a visual representation of an organization’s strategy that shows the cause-and-effect relationship between the components of the strategy . It helps to develop highly effective strategies, communicate them, and align them with the mission, vision, and goals . Strategy maps are not only easier to understand but also open up opportunities for everyone in the organization, from top to bottom, to get more involved during the design process . They are a great language that organizations can use to communicate their strategies, direction, and priorities .
A generic strategy map focuses on four strategic perspectives: Financial, Customer, Internal Processes, and Learning and Growth . The financial perspective is concerned with the financial objectives of the organization, such as revenue growth, profitability, and cost reduction . The customer perspective is concerned with the customer objectives of the organization, such as customer satisfaction, customer retention, and market share . The internal processes perspective is concerned with the internal processes of the organization, such as operational efficiency, quality, and innovation . The learning and growth perspective is concerned with the learning and growth objectives of the organization, such as employee satisfaction, employee development, and organizational culture .
The strategy map is designed to help a management team explore and discuss the strategy in more detail than they normally would . It helps develop highly effective strategies that can actually be implemented . In addition, strategy maps help those who are involved to develop the mission, vision, and goals, and action plans to address them, as well as understand the challenges they may face during the journey . Strategy maps also help discover strategic issues that are not necessarily obvious, be effective in evaluating organizational vision, mission, goals, strategies, and actions, communicate strategies in an easy-to-understand
Lean Six Sigma
Lean Six Sigma is a process improvement approach that uses a collaborative team effort to improve performance by systematically removing operational waste and reducing process variation. It combines Lean Management and Six Sigma to increase the velocity of value creation in business processes.
Lean Management focuses on eliminating the eight kinds of waste (muda), such as overproduction, waiting, defects, inventory, etc. Six Sigma focuses on improving process output quality by identifying and removing the causes of defects (errors) and minimizing variability in (manufacturing and business) processes.
Lean Six Sigma uses the Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve and Control (DMAIC) phases similar to that of Six Sigma. The five phases aim to identify the root cause of inefficiencies and work with any process, product, or service that has a large amount of data or measurable characteristics available.
Lean Six Sigma also uses different levels of certifications, divided into belt colors. The highest level of certification is a black belt, signifying a deep knowledge of Lean Six Sigma principles. Below the black belt are the green and yellow belts.
Lean Six Sigma is a fact-based, data-driven philosophy of improvement that values defect prevention over defect detection. It drives customer satisfaction and bottom-line results by reducing variation, waste, and cycle time, while promoting the use of work standardization and flow, thereby creating a competitive advantage.

Personal Development Planning
Personal Development Planning (PDP) is a structured approach to self-improvement and growth. It is a process that involves setting goals, identifying areas for improvement, and creating an action plan to achieve those goals. PDP is a lifelong process that can help individuals achieve their full potential and improve their overall well-being.
The process of creating a PDP typically involves several steps. The first step is to identify areas for improvement. This can be done by reflecting on past experiences, assessing current skills and knowledge, and considering future goals. Once areas for improvement have been identified, the next step is to set goals. Goals should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). This means that they should be clear, quantifiable, realistic, relevant to the individual’s needs, and have a deadline for completion.
After setting goals, the next step is to create an action plan. An action plan outlines the steps that need to be taken to achieve the goals. It should include specific actions, timelines, and resources needed to achieve the goals. The action plan should be reviewed regularly to ensure that progress is being made and to make any necessary adjustments.
PDP can be used in a variety of contexts, including personal, educational, and professional development. In personal development, PDP can help individuals identify areas for improvement and set goals to achieve personal growth. In educational settings, PDP can help students identify areas for improvement and set goals to achieve academic success. In professional development, PDP can help individuals identify areas for improvement and set goals to achieve career success.
There are several benefits to using PDP. PDP can help individuals identify their strengths and weaknesses, set goals, and create an action plan to achieve those goals. It can also help individuals improve their self-awareness, self-confidence, and overall well-being. PDP can also help individuals stay motivated and focused on achieving their goals.
In conclusion, Personal Development Planning is a structured approach to self-improvement and growth. It involves setting goals, identifying areas for improvement, and creating an action plan to achieve those goals. PDP is a lifelong process that can help individuals achieve their full potential and improve their overall well-being. By using PDP, individuals can identify their strengths and weaknesses, set goals, and create an action plan to achieve those goals. PDP can help individuals improve their self-awareness, self-confidence, and overall well-being, and stay motivated and focused on achieving their

Delegate tasks to capable team members to distribute workload and expedite progress
Delegate tasks to capable team members to distribute workload and expedite progress. Collaboration accelerates success. #Delegation #Teamwork
Embrace challenges as opportunities for growth
Embrace challenges as opportunities for growth. Don’t shy away from difficult tasks; tackle them head-on and prove your capabilities. #CareerGrowth #Challenges
Types Of Kpi Indicators
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) are quantifiable goals that measure the scope or potential of a companys success or attainable business objectives. They can help indicate which components of your business are the most beneficial to its progress, which ones can help optimize its performance, or which areas of your company may need work. There are various types of KPIs that can help measure the performance or progress of your business. Some of the most common types of KPIs include:
1. Quantitative indicators: These are represented by continuous or discrete numbers, which can be ratios, percentages, or whole numbers that represent values like rating scales, dollars, or weight. These indicators are the most straightforward quantifiable measures of performance, as they present direct numerical values.
2. Qualitative indicators: These indicators are not expressed numerically but through feelings or opinions. An employee satisfaction survey can be an example of qualitative data where performance is based on feedback.
3. Leading indicators: These are variables that can help identify long-term trends and possibly predict successful future outcomes of your business processes.
4. Lagging indicators: These compare a business current performance in a particular field with their past performance in the same field.
5. Input indicators: These track the resources necessary to produce the intended outcome, such as funding or extra staff. Input indicators can help companies keep track of how efficiently they are using their resources.
6. Output indicators: These measure the success or failure of your business activities, like the number of goods or services created through a particular process. Revenue growth and new customer acquisition also indicate how well your business is performing.
7. Process indicators: These represent the efficiency of a businesss process and how effectively it is functioning.
8. Practical indicators: These explore the function of an existing process at a company, usually involving observation or feedback on that process.
9. Directional indicators: These help determine the companys success in comparison with competitors, while practical indicators are specific to the companys process within itself.
10. Financial Metrics and KPIs: These are tied to the financials typically focus on revenue and profit.
11. Customer Experience Metrics and K

Practice effective communication to ensure clarity and alignment among team members, expediting progress towards shared objectives
Practice effective communication to ensure clarity and alignment among team members, expediting progress towards shared objectives. #Communication #Efficiency
Workforce Planning Cycle
Workforce Planning Cycle is a process of aligning the human resources of an organization with its strategic goals and objectives. It involves analyzing the current and future workforce needs, identifying the gaps and risks, developing and implementing action plans, and monitoring and evaluating the outcomes. Workforce Planning Cycle can be divided into two types: strategic and operational. Strategic workforce planning focuses on the long-term vision and direction of the organization, while operational workforce planning addresses the immediate and short-term priorities and challenges.
The following is a possible outline of an essay on Workforce Planning Cycle, with the approximate word count for each section:
– Introduction (100 words): Define Workforce Planning Cycle and its importance for organizational success. Provide the main thesis statement and the scope of the essay.
– Body (800 words): Discuss the steps and components of Workforce Planning Cycle, using examples and evidence from the web search results. You can use the following structure:
– Step 1: Set strategic direction (150 words): Explain how to align the workforce planning with the organizational vision, mission, values, and goals. Use [this source](^1^) as a reference.
– Step 2: Analyze workforce, identify skill gaps, and conduct workforce analysis (150 words): Explain how to assess the current and future supply and demand of talent, skills, and capabilities. Use [this source](^2^) as a reference.
– Step 3: Develop action plan (150 words): Explain how to design and prioritize strategies and solutions to address the workforce gaps and risks. Use [this source](^3^) as a reference.
– Step 4: Implement action plan (150 words): Explain how to execute and communicate the action plan, involving stakeholders and ensuring alignment and support. Use [this source](^4^) as a reference.
– Step 5: Monitor and evaluate progress (200 words): Explain how to measure and report the outcomes and impacts of the workforce planning, using indicators and feedback. Use [this source](^2^) as a reference.
– Conclusion (100 words): Summarize the main points and findings of the essay. Restate the thesis statement and provide recommendations and implications for future practice.

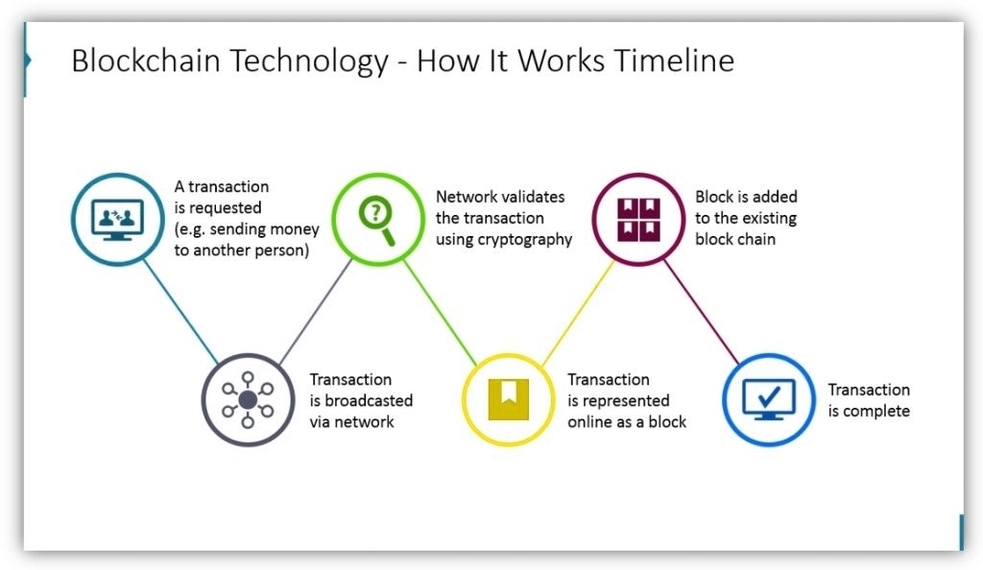
How Technology Works Blockchain
Blockchain is a technology that allows data to be stored and exchanged on a peer-to-peer network, without the need for a central authority or intermediary. Blockchain can be used for various purposes, such as creating cryptocurrencies, decentralized applications, smart contracts, and digital assets. Here is a brief overview of how blockchain works and some of its benefits and challenges.
A blockchain is essentially a distributed database or ledger that records transactions or events in a secure and transparent way. Each transaction or event is stored in a data structure called a block, which contains information such as the sender, the receiver, the amount, the timestamp, and a unique identifier called a hash. A hash is a string of numbers and letters that is generated by applying a mathematical function to the data in the block. The hash serves as a digital fingerprint that verifies the authenticity and integrity of the block.
Blocks are linked together in a chronological order, forming a chain of blocks, hence the name blockchain. Each block contains the hash of the previous block, creating a connection that cannot be altered or tampered with. This makes the blockchain immutable, meaning that once data is recorded, it cannot be changed or deleted. The blockchain is also distributed, meaning that it is shared and synchronized among multiple nodes or computers on the network. Each node has a copy of the entire blockchain and can validate new blocks and transactions. This eliminates the need for a central authority or intermediary to verify and process the data, and ensures that the blockchain is consistent and up-to-date across the network.
One of the main applications of blockchain is to create cryptocurrencies, such as Bitcoin, Ethereum, and Dogecoin. Cryptocurrencies are digital currencies that use cryptography to secure and regulate their creation and transfer. Cryptocurrencies operate on a peer-to-peer network, where users can send and receive payments directly, without the involvement of banks or intermediaries. Cryptocurrencies use blockchain to record and validate transactions, and to prevent double-spending, counterfeiting, and fraud. Cryptocurrencies also use a mechanism called consensus to achieve agreement among the nodes on the state of the blockchain. Consensus ensures that only valid blocks and transactions are added to the blockchain, and that malicious or conflicting blocks and transactions are rejected. There are different types of consensus algorithms, such as proof-of-work, proof-of-stake, and proof-of-authority, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
Another application of blockchain is to create decentralized applications, or dApps, which are